centos下配置vsftpd虚拟用户教程[整理]
点击下载vsftp_install.sh一键安装脚本:vsftpd_install.sh
基本配置环境如下:
1.ftp用户的home目录:/data/ftp
2.所有虚拟用户的local_root目录,都放在/data/wwwroot/这里.这里为了方便,目录名和虚拟用户名一样,当然也可以不一样的
3.允许登录用户文件:/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list
==========================================
1.安装vsftpd
#yum -y install vsftpd
可用service vsftpd start 命令查看是否安装成功
设置CentOS vsftpd自启动
#chkconfig --level 35 vsftpd on
2.配置vsftpd.conf文件
#vi /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
anonymous_enable=NO 是否允许匿名用户访问
#chroot_list_enable=YES 限定用户不可以离开主目录
#chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_listchroot_local_user=YES //这里为了方便,直接默认情况下将所有用户都锁定在自己的目录里,如果不写这一行的话,就需要启用上面的两行,以后添加新账户的时候需要将用户添加到chroot_list_file来,来进行锁定用户在自己的目录里,参考:http://blog.haohtml.com/archives/857
local_enable=YES/NO 本地用户是否可以访问 注:如果为NO 则所有虚拟用户都将不能访问原因:虚拟用户访问在主机上其实是以本地用户访问的
pam_service_name=vsftpd pam认证文件名 在/etc/pam.d/vsftpdguest_enable=YES 启用虚拟用户功能
guest_username=ftpadmin 指定虚拟用户的宿主用户 –centos 里面已经有内置的ftp用户了,这里我们使用重新创建的用户(注:此用户在chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list文件里所指定的用户)user_config_dir=/etc/vsftpd/vuser_conf 设置虚拟用户个人vsftp的服务配置文件所在目录
vsftpd用户没有办法修改文件的权限的权限(chmod),加上这两行就可以了http://blog.haohtml.com/archives/7852
virtual_use_local_privs=YES
chmod_enable=YES
创建虚拟用户配置文件目录
#mkdir /etc/vsftpd/vuser_conf
#mkdir /etc/vsftpd/chroot_list
四.在认证文件chroot_list里添加vsftpd虚拟用户所对应的本地系统用户
创建vsftpd运行用户ftpadmin,在创建前请确认是否有/data目录,没有的话创建一个,或者最后创建这个目录,把权限分配一下也可以(这里为了配合web使用,并没有使用默认的ftp:ftp用户)
#/usr/sbin/useradd -d /data/ftp -g www -s /sbin/nologin ftpadmin
#passwd ftpadmin
这里说明一下,如果您在前面vsftpd.conf文件里使用的是chroot_local_user=YES指令的话,则下面的一步操作可以直接跳过去,否则需要把ftpadmin写到chroot_list文件里才可以.
将ftpadmin添加到/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list文件中
#vi /etc/vsftpd/chroot_list
ftpadmin
五.创建虚拟用户并生成虚拟用户db文件
安装相应的库
#yum -y install db4-utils
添加虚拟用户,(奇数行为用户名 ,偶数行为密码)
#vi /etc/vsftpd/vftpuser.txt
zz
aaaaa
ftp1
zzzzz
生成db文件
#db_load -T -t hash -f /etc/vsftpd/vftpuser.txt /etc/vsftpd/vftpuser.db
六.生成认证文件文件
#vi /etc/pam.d/vsftpd
auth required pam_userdb.so db=/etc/vsftpd/vftpuser
account required pam_userdb.so db=/etc/vsftpd/vftpuser
如果使用的是64位系统,要增加以下两句:
auth required /lib64/security/pam_userdb.so db=/etc/vsftpd/vftpuser
account required /lib64/security/pam_userdb.so db=/etc/vsftpd/vftpuser
注:这里db=/etc/vsftpd/vftpuser 中的vftpuser 是你生成的虚拟用户的db文件.
/etc/pam.d/vsftpd文件里的默认内容可以先注释掉.添加上面两行内容.
七.创建每个虚拟用户的配置文件(配置文件所在目录为/etc/vsftpd/vuser_conf,用户必须为vftpuser.txt中的用户)
这里假如添加的虚拟用户名为zz,创建的文件是以虚拟ftp用户为文件名
# vi /etc/vsftpd/vuser_conf/zz
local_root=/data/wwwroot/zzftp(虚拟用户的根目录根据实际修改)
write_enable=YES (可写)
download_enable=YES
anon_world_readable_only=NO
anon_upload_enable=YES
anon_mkdir_write_enable=YES
anon_other_write_enable=YES
local_umask=022
listen_port=21
创建ftp虚拟用户目录,并给虚拟ftp用户目录修改权限
#mkdir -p /data/wwwroot/zzftp
#chown -R ftpadmin:www /data/wwwroot/zzftp
#chmod -R 775 /data/wwwroot/zzftp
注意上面的目录权限值是775,因为和web一块使用,这里ftpadmin也是www一个组的,所以要有组用户的权限才可以.
七.重启vsftpd
#service vsftpd restart
#setsebool ftpd_disable_trans 1
八.测试虚拟用户
# ftp192.168.1.107
Connected to 192.168.1.107.
220 (vsFTPd 2.0.5)
530 Please login with USER and PASS.
530 Please login with USER and PASS.
KERBEROS_V4 rejected as anauthentication type
Name (192.168.1.107:root): zz
331 Please specify the password.
Password:
500 OOPS: cannot changedirectory:/data/wwwroot/zzftp
Login failed.
ftp>
查看方法
# getenforce
Enforcing 如果出现(Enforcing )
关闭方法:
#setenforce 0 (0|1 开|关)或者
setsebool ftpd_disable_trans 1
命令也可以.
这时,你也可以用flashxp软件来测试一下,包括文件和文件夹的权限的变更,上传和删除,重命名命令之类的.
注意:这里目前只有两个虚拟用户,如果要添加新的虚拟用户的话,需要先在/etc/vsftpd/vftpuser.txt里添加,然后再重新用"#db_load -T -t hash -f /etc/vsftpd/vftpuser.txt /etc/vsftpd/vftpuser.db"命令重新生成db库.不过可以写成一个shell来解决这个问题的.
如果登录的时候出现" 500 OOPS: reading non-root config file"错误,只需要将在user_conf/下的配置文件owner改为root 即可.有次我重装安装vsftpd.将上次的配置文件下载到本机上,装好vsftpd,直接将配置覆盖了一下.出现这个问题了.大家以后要注意一下.
为了后面的测试,这们这里上传一个blog程序wordpress.
九.测试web站点
至此为此我们已经把vsftp方面做的差不多了,下面我们来用这个ftp目录来做为网站的根目录,测试一下.这里我用的是Nginx的.如果您用的是apache或者其它类的,请根据实际情况来修改.
这里我采用的是nginx的include指令来添加虚拟主机站点配置信息的,比较的灵活,参考:http://blog.haohtml.com/archives/6203
在/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf文件里添加了一行 include /usr/local/nginx/conf/vhost/*.conf; (注意不要忘记最后的分号)这样添加虚拟主机站点配置文件时,只需要在/usr/local/nginx/conf/vhost/ 目录里创建一个以.conf为扩展名的文件即可.
vi /usr/local/nginx/conf/vhost/www.haohtml.com.conf
server {
listen 80 default;
server_name www.haohtml.com;
root /data/wwwroot/zzftp;location / {
index index.php index.html index.shtml;
}location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /data/wwwroot/zzftp$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}#log...
}
配置内容如上.
十.测试站点
#/usr/local/php/sbin/php-fpm start
#/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t //测试配置是否正确
#killall nginx
#/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
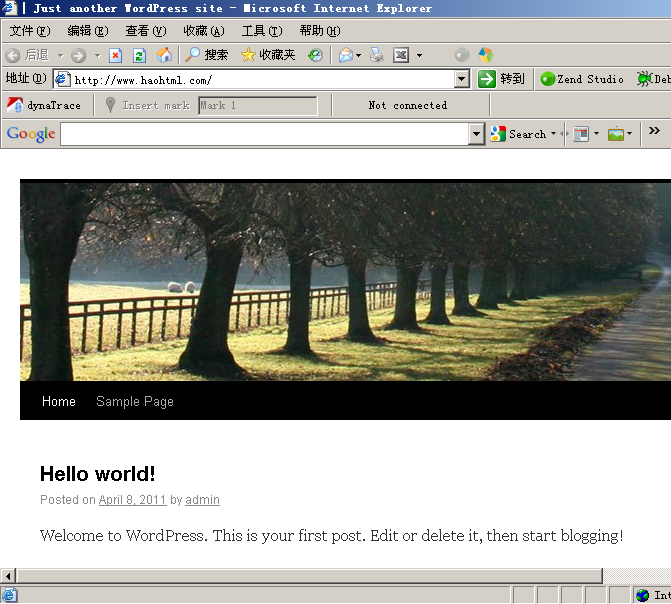
在浏览器里打开http://www.haohtml.com就会看到这样的页面
对于CentOS5.5下安装NGINX+MYSQL+PHP+MEMCACHE的方法请参考:http://blog.haohtml.com/archives/6051
/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf文件:
# The default compiled in settings are fairly paranoid. This sample file # loosens things up a bit, to make the ftp daemon more usable. # Please see vsftpd.conf.5 for all compiled in defaults. # # READ THIS: This example file is NOT an exhaustive list of vsftpd options. # Please read the vsftpd.conf.5 manual page to get a full idea of vsftpd's # capabilities. # # Allow anonymous FTP? (Beware - allowed by default if you comment this out). anonymous_enable=NO # # Uncomment this to allow local users to log in. local_enable=YES # # Uncomment this to enable any form of FTP write command. write_enable=YES # # Default umask for local users is 077. You may wish to change this to 022, # if your users expect that (022 is used by most other ftpd's) local_umask=022 # # Uncomment this to allow the anonymous FTP user to upload files. This only # has an effect if the above global write enable is activated. Also, you will # obviously need to create a directory writable by the FTP user. #anon_upload_enable=YES # # Uncomment this if you want the anonymous FTP user to be able to create # new directories. #anon_mkdir_write_enable=YES # # Activate directory messages - messages given to remote users when they # go into a certain directory. dirmessage_enable=YES # # The target log file can be vsftpd_log_file or xferlog_file. # This depends on setting xferlog_std_format parameter xferlog_enable=YES # # Make sure PORT transfer connections originate from port 20 (ftp-data). connect_from_port_20=YES # # If you want, you can arrange for uploaded anonymous files to be owned by # a different user. Note! Using "root" for uploaded files is not # recommended! #chown_uploads=YES #chown_username=whoever # # The name of log file when xferlog_enable=YES and xferlog_std_format=YES # WARNING - changing this filename affects /etc/logrotate.d/vsftpd.log #xferlog_file=/var/log/xferlog # # Switches between logging into vsftpd_log_file and xferlog_file files. # NO writes to vsftpd_log_file, YES to xferlog_file xferlog_std_format=YES # # You may change the default value for timing out an idle session. #idle_session_timeout=600 # # You may change the default value for timing out a data connection. #data_connection_timeout=120 # # It is recommended that you define on your system a unique user which the # ftp server can use as a totally isolated and unprivileged user. #nopriv_user=ftpsecure # # Enable this and the server will recognise asynchronous ABOR requests. Not # recommended for security (the code is non-trivial). Not enabling it, # however, may confuse older FTP clients. #async_abor_enable=YES # # By default the server will pretend to allow ASCII mode but in fact ignore # the request. Turn on the below options to have the server actually do ASCII # mangling on files when in ASCII mode. # Beware that on some FTP servers, ASCII support allows a denial of service # attack (DoS) via the command "SIZE /big/file" in ASCII mode. vsftpd # predicted this attack and has always been safe, reporting the size of the # raw file. # ASCII mangling is a horrible feature of the protocol. #ascii_upload_enable=YES #ascii_download_enable=YES # # You may fully customise the login banner string: #ftpd_banner=Welcome to blah FTP service. # # You may specify a file of disallowed anonymous e-mail addresses. Apparently # useful for combatting certain DoS attacks. #deny_email_enable=YES # (default follows) #banned_email_file=/etc/vsftpd/banned_emails # # You may specify an explicit list of local users to chroot() to their home # directory. If chroot_local_user is YES, then this list becomes a list of # users to NOT chroot(). #chroot_list_enable=YES # (default follows) #chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list # # You may activate the "-R" option to the builtin ls. This is disabled by # default to avoid remote users being able to cause excessive I/O on large # sites. However, some broken FTP clients such as "ncftp" and "mirror" assume # the presence of the "-R" option, so there is a strong case for enabling it. #ls_recurse_enable=YES # # When "listen" directive is enabled, vsftpd runs in standalone mode and # listens on IPv4 sockets. This directive cannot be used in conjunction # with the listen_ipv6 directive. listen=YES # # This directive enables listening on IPv6 sockets. To listen on IPv4 and IPv6 # sockets, you must run two copies of vsftpd whith two configuration files. # Make sure, that one of the listen options is commented !! #listen_ipv6=YES
pam_service_name=vsftpd
userlist_enable=YES
tcp_wrappers=YES
chroot_local_user=YES
guest_enable=YES
guest_username=ftpadmin
user_config_dir=/etc/vsftpd/vuser_conf
virtual_use_local_privs=YES
chmod_enable=YES
对于我的vsftpd配置文件见:vsftpd.conf